Prevention of helminthsconsists of adhering to strict hygiene rules. Many of us do not realize that we are infected with many parasites. Fatigue, apathy, headaches, and poor digestion are often caused by overwork or food quality. And some people think that these symptoms may indicate a parasitic attack.
The worst thing is that helminthiases are hidden, slowly affecting our health. The risk group includes children, whose bodies are often powerless to fight parasites. Therefore, it is very important to prevent worms in a natural way, with the help of immunity.
Helminths and harm to the body
Worm attacks in humans can be caused by more than 400 species of parasitic worms. Infections often occur through contaminated food and water, less often helminths penetrate the body through the skin.
Depending on the route of infection, parasites are divided into 3 groups:
- biohelminths- through food (echinococcus, cattle and pig tapeworms);
- geohelminths- with hands contaminated with feces, household items, sometimes water (whip worms, tapeworms, ringworms);
- Call the worm- with personal contact with infected people, less often with self -infection (pinworms, dwarf tapeworms).
According to body structure, parasites are divided into the following types:
- round (nematode);
- pita (cestodes);
- flukes (has a strong suction and a flat body).
Risk groups include children attending preschool institutions, agricultural workers, patients with immune deficiencies, the elderly and the elderly. Pets can also be at risk of infection.
In adults, helminthiases often occur latently (hidden), have a protracted course and manifest themselves with a variety of clinical signs disguised as distinct pathologies. Children are characterized by an acute course with obvious symptoms, which are associated with abnormalities of the immune system.
Helminths use the human body as a source of food, habitat and reproduction. On the other hand, releasing the products of their vital activity, worms cause systemic toxic damage to human organs and systems.
For example, the larvae of mineworms secrete anticoagulants to maintain blood flow. It is estimated that A. duodenale alone causes 0. 2 ml of blood loss per day. To lose 5 ml of blood, the presence of 25 pieces of helminths in the body is sufficient. But there are usually more of them. As a result, infected people develop severe anemia.
According to many studies, helminthic invasion contributes to the development of more frequent somatic diseases, exacerbation of chronic pathology, has a negative impact on the host body, including his immune system.
Characteristic of most helminthiases is a chronic course associated with the prolonged presence of pathogens in the body and recurrent recurrent infections. Helminthiasis in children is often accompanied by a variety of nonspecific symptoms: weakness, fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances, dyspepsia, growth retardation and weight gain, and decreased immunity.
Diseases caused by helminths reduce the ability to work and worsen the quality of life.
The role of immunity to helminths
The immune system is always on the lookout for our health. It protects the body from the entry of viruses, bacteria and parasites. Unfortunately, immunity overcomes the latter even worse. This is especially true for children. Children’s defenses are not sufficiently developed, and helminthic invasion continues to impair the body’s resistance to infection. Therefore, the prevention of helminths for children is very important.

Antiparasitic immunity is similar to antibacterial immunity. Both cellular and humoral links are involved in protection against helminths. The first barrier for the invader is the skin and mucous membranes. More often, worms enter the body through the digestive tract. The mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines contain immune cells that trigger a response to repel parasites and remove them from the body.
The problem is that helminths have their own defense mechanisms, which often allow them to easily get past the first obstacle.
Immunity to helminths is divided into primary and secondary. Since the main person is born, he or she is a genetically determined defense factor. Secondary is formed during life after infection and the production of specific antibodies against certain types of parasites.
The recently discovered TSLP (Thymus Stromal Lympopoietin) has aroused great interest among scientists. Due to their unique properties, cytokines play an important role in protecting the body from worms. Depending on the nature of the infection, TSLP can enhance or inhibit the defense response controlled by two types of T-lymphocytes.
The likelihood of infection largely depends on the innate immunity and the health of the immune system as a whole, its effectiveness is always individual, and depends on the type of worm.
The good function of the immune system depends on our diet, if the body lacks the vitamins and minerals needed to build immune cells, then the response to infection will be weak and the fight will end in defeat.
Immunity requires biologically active substances that come to us with food. In case of stress or chronic illness, it is important to support the immune system with vitamins and micro -elements, because the body uses all the nutrients to strengthen the nervous system, as well as herbs. And only in severe cases, use drug treatment.
How does immunity to worms work?
Primary immunity to helminths can work in several ways:
- Parasites adapt to the internal environment of the host organism, grow well, grow, reproduce. The immune response is minimal. In such cases, helminthiases are long -term, sometimes difficult. An example is the invasion of dwarf tapeworms.
- A mild immune response appears on the introduction of helminths. This limits the fertility of the worms. For example, bracelet worms.
- The defensive reaction is well expressed, which prevents the full development of the parasite. Worms do not reach sexual maturity, but they can be harmful to health. The disease is short -lived or takes a latent course.
- Effective primary immunity stops the introduction of parasites at the level of the skin and mucous membranes. As a result, helminths do not penetrate internal organs and do not endanger health.
Secondary immunity helps the body respond more quickly and more effectively to recurrent helminthic invasions. This inhibits the development of worms in the first stages of infection and reduces the toxic effects. The protective response is based on the presence in the blood of antibodies (immunoglobulins) to this type of helminth.
The main links of immune defense against parasitic invasion:
- tissue reactions of internal organs, leading to isolation (capsule formation) and destruction of worms;
- production of class A and E immunoglobulins;
- changes in hormonal activity, especially on the part of estrogen, which are found in both the female and male bodies;
- hereditary factors (antiparasitic primary immunity).
An indicator of infection is a high content of eosinophils in the blood, which indicates an allergic reaction. The second important thing is a sharp increase in the concentration of immunoglobulin E, provided there is no food intolerance.
Important rules of prevention
Immunity overcomes the introduction of parasites in different ways, not always effectively enough. Our job is to help the body prevent the threat of alien invasion. Precautionary measures must be followed at all times and without exception.
Parents should teach their child from a young age the rules of personal hygiene to minimize the risk of infection.
Preventive measures are simple and accessible to everyone, while allowing you to completely (or almost completely) exclude the danger of helminthic invasion. However, doctors recommend that at-risk groups carry out additional prophylaxis with medications, despite all the measures that need to be taken. Medication is also taken as directed by the doctor if an infection is suspected or worms are detected during diagnosis.
Rules for the prevention of helminthiasis:
- Buy meat and fish products at designated locations. The seller must have a quality certificate and a health certificate.
- Cook enough food. Follow the rules of salting, canning and pickling.
- Drink tap water or filtered water.
- Wash vegetables and fruits under running water before use. Vegetables can be rinsed first with soapy water and then rinsed with clean water. Strawberries are soaked in a 1%soda solution. After the berries are washed with running water. Vegetables heavily contaminated with fertilizers are recommended to be soaked first in a weak solution of iodine (not more than 0. 3%).
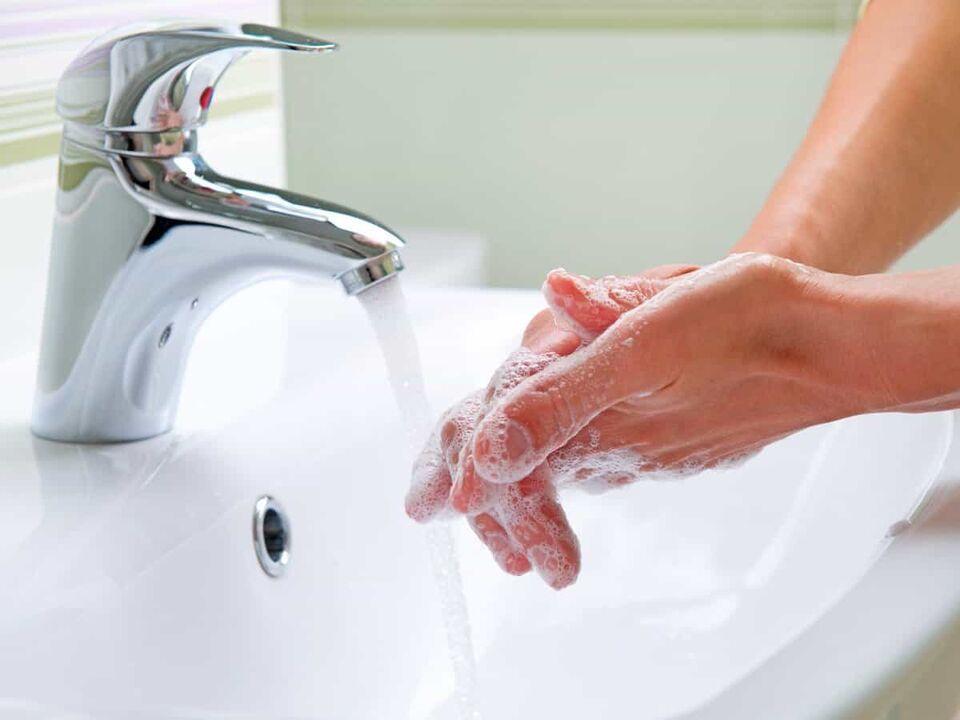
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene. Wash your hands with soap and water after using the toilet, outdoors, working in your garden area, after every contact with animals, including pets.
- Clean the area regularly with disinfectant, especially the bathroom and kitchen.
- Deworm pets according to a veterinarian's schedule (usually 1-2 times a year).
- In case of enterobiasis, pay special attention to hand and nail hygiene, wash the child at night and in the morning, each time changing the underwear and bed linen, which have been ironed with an iron. This prevents recurrence of self -infection.
- It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle to strengthen and maintain your immune system. Rational nutrition, regular physical activity, proper response to stress, and rejection of bad habits will reduce the risk of parasitic infections.
- Chemoprophylaxis 1-2 times a year according to the scheme prescribed by the doctor.

Medicine for worms is taken in pill form.This is chemoprophylaxis that aims to destroy parasites that may have entered the body, but did not have time to cause a response from the internal organs.
They have antihelminthic effectspumpkin seeds.Before eating, the seeds can be chopped and mixed with a little honey. The daily dose for adults is 300 grams, for children, depending on age. Up to 4 years - 80 grams, up to 7 years - 100 grams, up to 10 years - 150 grams, up to 15 years - 200 grams. After 3 hours, laxatives are taken.
Prevention of helminthiasis consists of strengthening the immune system, adhering to the rules of personal hygiene and culinary processing of products. By following simple rules, we can protect ourselves from worm infections. Annual chemoprophylaxis helps our immune system to cope with foreign attacks.
Talk to your doctor before taking antihelminthic medications. The specialist will select the appropriate medication for you and provide recommendations on treatment regimens. Uncontrolled reception is not only useless, but also endangers your health. Don't forget this.
The best alternative to pills is herbs from worms.



























